Competitive analysis, also known as competitive intelligence or competitor analysis, is the process of gathering and evaluating information about competitors in the same industry or market to gain insights into their strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and performance. This analysis helps businesses make informed decisions, refine their own strategies, and identify opportunities and threats in the competitive landscape. Here are the key components and steps involved in competitive analysis:
- Identifying Competitors:
- Begin by identifying who your primary and secondary competitors are in your industry or market. Primary competitors are those offering similar products or services to the same target audience, while secondary competitors may offer related or substitute products.
- Gathering Information:
- Collect data and information about your competitors through various sources, including:
- Publicly available information: This includes websites, annual reports, press releases, and regulatory filings.
- Online research: Analyze competitors’ online presence, including social media profiles, customer reviews, and online advertising.
- Customer feedback: Gather insights from customer reviews, testimonials, and surveys.
- Industry reports and news: Stay updated on industry news, trends, and reports related to your competitors.
- Trade shows and conferences: Attend industry events to gather information and observe competitors’ activities.
- Collect data and information about your competitors through various sources, including:
- Analyzing Products/Services:
- Evaluate your competitors’ products or services in terms of features, quality, pricing, and positioning. Identify any unique selling points (USPs) or advantages they have.
- Market Share and Positioning:
- Determine your competitors’ market share and their position in the market relative to your own. Understand how they are perceived by customers and whether they are considered leaders or niche players.
- Pricing Strategy:
- Analyze your competitors’ pricing strategies, including pricing models, discounts, and any special offers. Consider how your pricing compares and whether you can gain a competitive advantage.
- Marketing and Promotion:
- Examine competitors’ marketing tactics, advertising campaigns, and promotional efforts. Look for patterns in messaging, channels, and frequency.
- Distribution Channels:
- Understand how competitors distribute their products or services. This includes identifying their distribution partners, channels, and logistics.
- Customer Base:
- Investigate the demographics, behaviors, and preferences of your competitors’ customer base. Consider whether there are opportunities to target specific customer segments that your competitors may be overlooking.
- SWOT Analysis:
- Conduct a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) for each competitor. Identify their internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats in the market.
- Benchmarking:
- Compare your own business’s performance and metrics to those of your competitors. This can help identify areas where you need improvement.
- Strategy Evaluation:
- Assess your competitors’ strategic initiatives, such as expansion plans, new product launches, or partnerships. Understand how these strategies may impact your own business.
- Risk Assessment:
- Identify potential risks and threats posed by competitors, such as aggressive pricing or disruptive innovations. Develop strategies to mitigate these risks.
- Continuous Monitoring:
- Competitive analysis is an ongoing process. Regularly update your information and insights to stay current with changes in the competitive landscape.
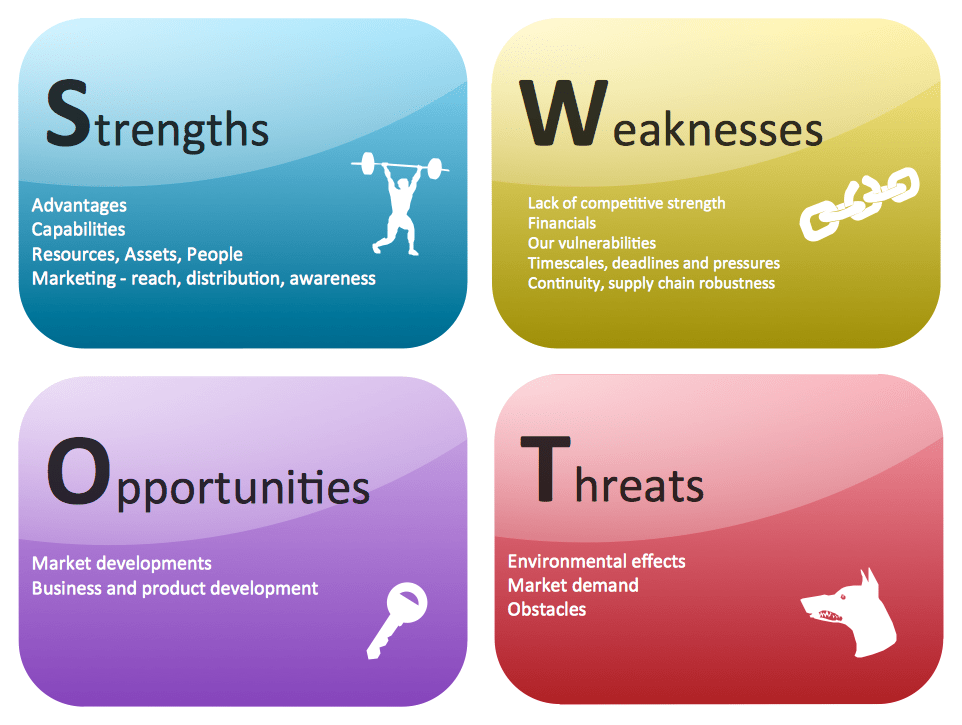
Competitive analysis is a valuable tool for strategic planning and decision-making. It helps businesses identify opportunities for growth, areas where they can differentiate themselves, and potential challenges they may face in the marketplace. By understanding their competitors, businesses can adapt and refine their own strategies to remain competitive and successful.
